SB. Why keeping a lemon in your bedroom is a great idea
Lemons (Citrus limon), native to northeastern India and widely cultivated across the globe, are a rich source of vitamin C, antioxidants, and essential oils. According to the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA), a single lemon provides around 31 mg of vitamin C, which is about 51% of the recommended daily intake for adults [USDA FoodData Central].
Vitamin C is essential for immune function, skin health, and the neutralization of free radicals. Lemons also contain bioactive compounds like flavonoids, limonene, and citric acid, which have been studied for their antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties [NIH: National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI)].
Why Place a Lemon in Your Bedroom?
Some home wellness advocates recommend placing a cut lemon in the bedroom overnight. Though this idea may seem unusual at first, there are some practical and scientific explanations behind the practice.
1. Natural Air Freshening and Purification
Lemons emit a clean, citrus aroma thanks to their essential oil content—particularly limonene, a compound found in the peel. Research published in the journal Molecules shows that limonene has antimicrobial and antifungal properties [Molecules, MDPI, 2018].
While a lemon placed in a room won’t disinfect it entirely, the volatile compounds it releases can mildly reduce airborne bacteria and unpleasant odors, functioning as a natural air freshener.
2. Promotes Relaxation and Sleep Quality
While limited, some studies suggest that citrus scents may have mild calming effects on the nervous system. A review published in Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine found that certain essential oils, including those derived from citrus fruits like lemon, may help reduce anxiety and promote sleep in some individuals [PMC5960960].
This effect is typically stronger when using concentrated essential oils in aromatherapy. However, the subtle scent released from a cut lemon may also help create a more soothing bedroom environment for some people.
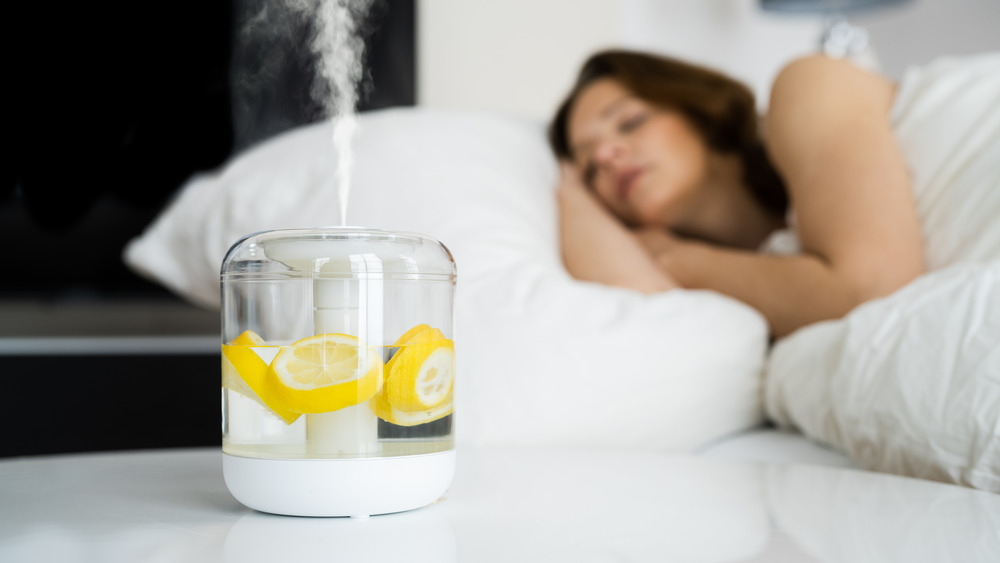

3. Supports Respiratory Comfort
The fresh scent of lemon can potentially assist with mild sinus discomfort. Though not a substitute for medical treatment, the vapor from citrus oils may help clear nasal passages and support easier breathing. According to a study in the Journal of Ethnopharmacology, certain citrus compounds exhibit expectorant properties that may be useful for relieving mild congestion [Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 2009].
It’s worth noting that this effect is more pronounced when lemon oil is used in steam inhalation rather than simply placing a lemon in the room. However, individuals with seasonal allergies or mild colds might find the scent soothing.
Additional Benefits of Lemon (with Scientific Backing)
Aside from their use as room fresheners, lemons offer several health benefits when consumed as part of a balanced diet:
4. Supports Immune Function
Vitamin C in lemons enhances the function of immune cells and strengthens the skin’s defense system. Regular intake may reduce the duration and severity of colds, as confirmed by multiple studies reviewed in the Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews [CDSR, 2013].
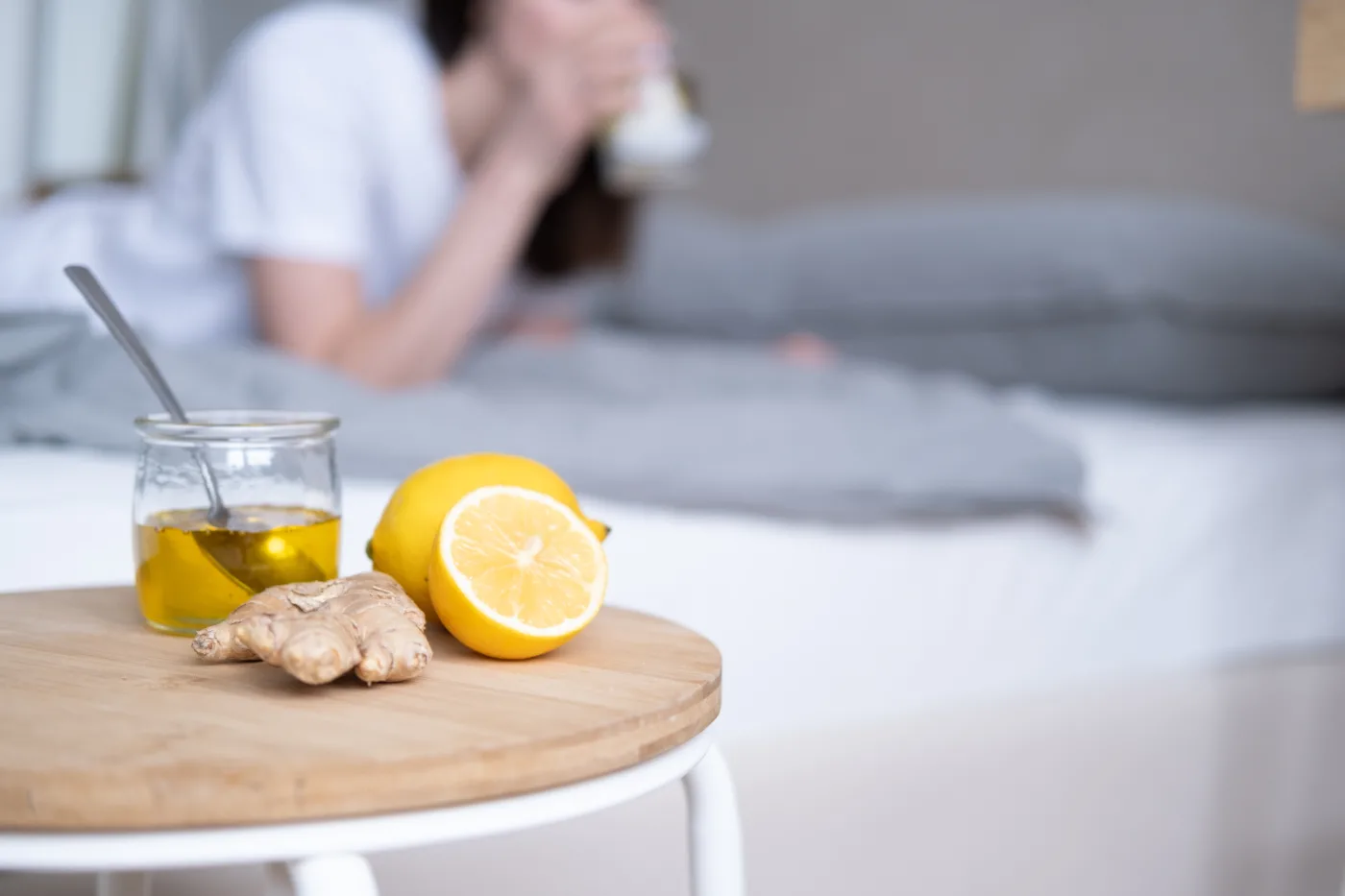

5. May Aid Digestion
Lemon juice, particularly when mixed with warm water, is a popular home remedy for digestive discomfort. Though not a cure-all, its acidity may support healthy stomach function and stimulate saliva and gastric juices, aiding the digestive process [Harvard Health Publishing].
6. Promotes Hydration
Adding lemon to water can make it more appealing, encouraging people to drink more fluids. Proper hydration supports energy levels, cognitive function, and metabolism.
7. Rich in Antioxidants
The flavonoids found in lemon peel and pulp have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. These compounds may help protect cells from oxidative stress, which is associated with aging and chronic disease [NCBI, 2010].

Addressing Common Myths
It’s important to distinguish between anecdotal tips and scientifically verified health claims. Some websites claim that lemons placed in the bedroom can “detox the air,” cure asthma, or even lead to dramatic weight loss. These claims are not substantiated by scientific evidence.
- Lemon and Weight Loss: While lemons can support hydration and may be part of a healthy diet, there is no evidence that merely smelling or placing lemons in your environment can lead to weight loss.
- Lemon as an Insect Repellent: Certain studies suggest that lemon oil and limonene may repel some insects, including mosquitoes, when applied to the skin or used in concentrated sprays. However, placing a lemon in the room is unlikely to provide significant protection [Journal of the American Mosquito Control Association].
- Lemon and Allergies: While the scent of lemon may feel soothing, it does not cure allergies. In fact, individuals with citrus sensitivity or strong environmental allergies should exercise caution when using citrus scents or oils indoors.
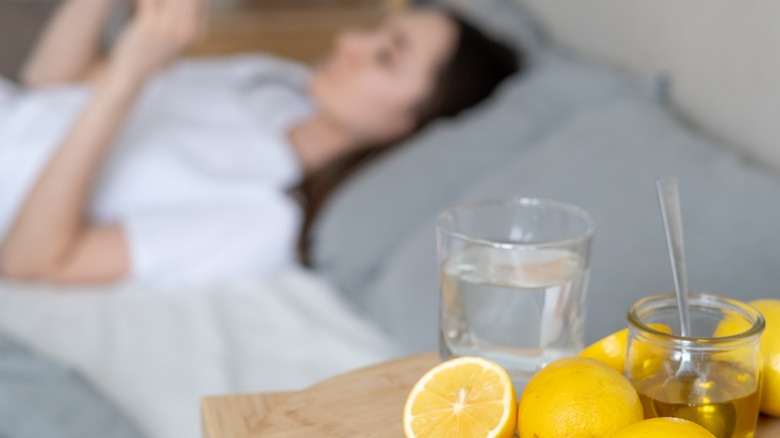

How to Use Lemons in Your Room Safely
If you want to try using lemon as a natural freshener or calming agent, here are some tips:
- Slice a fresh lemon into quarters and place it on a small plate or bowl on your bedside table.
- Replace it daily to prevent bacterial growth or mold.
- Avoid placing lemon slices near heat or vents, as this can dry them out quickly and reduce scent emission.
- Use lemon essential oil in a diffuser if you’re looking for a stronger aroma with more consistent benefits.
Final Thoughts
While placing a lemon in your bedroom won’t dramatically transform your health overnight, it can offer subtle wellness perks—from gently refreshing the air to supporting a relaxing sleep environment. When paired with other healthy habits, such small natural practices can contribute to a holistic sense of wellbeing.
Lemons remain a powerhouse of nutrients and beneficial plant compounds when consumed as part of a balanced diet. Whether you enjoy them in tea, in salad dressings, or simply as an aromatic accent in your home, lemons are a valuable addition to any lifestyle.
Sources:
- USDA FoodData Central: https://fdc.nal.usda.gov
- NIH – National Center for Biotechnology Information: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
- Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5960960
- Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews: https://www.cochranelibrary.com
- Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 2009: https://www.sciencedirect.com/journal/journal-of-ethnopharmacology
- Harvard Health Publishing: https://www.health.harvard.edu
- Journal of the American Mosquito Control Association: https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org